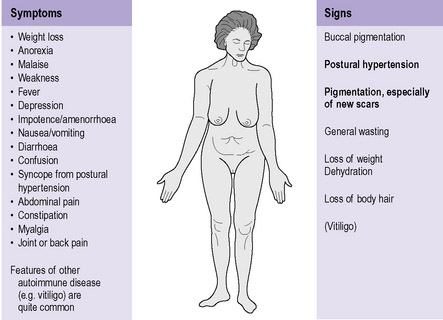
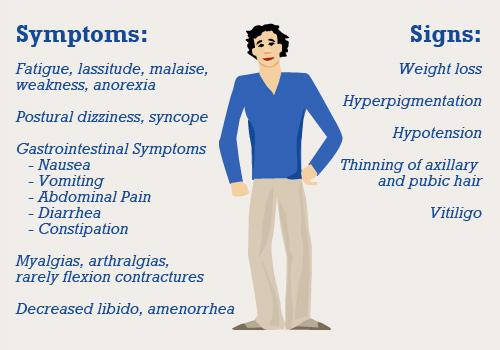
Addison's Disease is a hormonal disorder caused by excessive production of cortisol in the adrenal glands. This excessive production of cortisol can be caused by several risk factors: The main symptoms of Addison's Disease are: weight gain: Changes in blood sugar levels: Other symptoms: Tests: Treatment: Corticosteroid replacement therapy will treat the symptoms of the disease. Corticosteroid medications can be used to reduce the inflammation, reduce the edema and increase the secretion of cortisone. A medication such as prednisone and hydrocortisone can be used in mild Addison's Disease.
The effects of these corticosteroid drugs are reversible and usually take weeks before noticeable improvement is noted. Medications can be taken either orally or intravenously. There are several adverse side effects that can occur with long-term use of the medication. Corticosteroid medication is not effective for all patients; a test called the 'serum cortisol' is used to identify those who will respond to the treatment.
Corticosteroid therapy can stop Addison's Disease and make the symptoms better in the majority of cases. It will also relieve some of the pain associated with Addison's.
In Addison's Disease, the adrenal glands produce too much cortisol. The excess cortisol causes a build up of fluid in the body, causing a reduction in the body's ability to absorb nutrition.
Glucocorticoids are essential to the production of insulin in the body, which is needed to regulate the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates into energy. Glucocorticoids help increase the amount of energy your body uses to burn fat.
Glucocorticoids are produced by the adrenal glands and the pituitary gland. These glands produce glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids act on receptors in your brain, preventing the brain from making another hormone, ACTH. The adrenal gland is usually stimulated by injecting corticosterone into the pituitary gland. If the patient regularly takes glucocorticoids, there is an increased production of glucocorticoids in the liver and a disruption in the production of glucocorticoids and ACTH, which leads to excessive production of cortisol by the patient's adrenal glands.
Chronic glucocorticoids have side effects that can range from mild to severe. The most common side effect is fatigue and weakness in the legs and lower back.
Addison's disease is a disorder of the adrenal glands, but it can also be an endocrine disorder, especially Addison-Hicks disease. Addison Hicks occurs when the adrenal glands cannot produce enough of the hormone cortisol, which is produced by the liver.
When Addison's disease occurs, there is usually very little enzyme left in the adrenal glands. They are called adrenocorticotropin and glycogen.
In addition to reducing the production of cortisol, Addison's disease increases the production of glucocorticoids in the liver. In turn, glucocorticoids cause more pain.
Liver failure is common with Addison's disease. A patient with Addison's disease should be evaluated by a liver specialist, especially if the liver is not working properly or if the patient feels tired, fatigued, or depressed.
In addition to glucocorticoids, medications are prescribed to treat pain caused by Addison's disease. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are used to reduce pain and inflammation. They can also help control pain, reduce inflammation, and slow the healing process. This type of medication has many side effects, including liver problems.
If Addison's Disease has become too much for the person, it may be a sign of other chronic health problems, so the doctor will monitor the patient for these problems as well
For people with Addison's, surgery may be needed.
Some Addisons don't require surgery, but this doesn't mean they don't need treatment. The surgery may not correct everything that is wrong with Addison's. In some cases, there may not be anything to be done to stop the symptoms. The only sure way to know this is through medical testing.
In some cases, patients may find relief from physical therapy, diet, and exercise. Medications such as glucocorticosteroids can also be used.
Treatment of Addison's Disease is important for the general well being of the person who has it. This disease can take years to become totally eliminated, but by taking the right steps, it can be treated and the symptoms can be controlled.
